Embedded Files
ArmDot can embed files into protected assembly.
This feature is available on Windows only.
For example, you might need to merge unmanaged DLLs into your application in order to distribute a single executable file. Also, it's possible to hide and protect assets: media files, images, configuration files, databases, etc.
The assembly reads and writes to such a file as if it really existed on a disk. At the same time, embedded files are not saved to a disk, but located in process memory instead.
There are two ways to embed files: using a special attribute, ArmDot.Client.EmbedFileAttribute.
Embedding files by a declarative way
To embed a file this way, use ArmDot.Client.EmbedFileAttribute, instructing ArmDot where to get file content, and what is a file runtime path.
Runtime path can be a full path, but usually it consists of a predefined directory id and a relative path, that allows to place a file to the assembly directory, or to some system directory:
// AssemblyInfo.cs
using ArmDot.Client;
[assembly: EmbedFile(SourcePath: "file_content.txt", RuntimePath: @"$(AssemblyDirectory)\embedded_file.txt")]You can find a complete ready to use sample on GitHub: https://github.com/Softanics/armdot-sample-embed-file
Embedding files using the ArmDot UI
Switch to Files in the ArmDot UI:
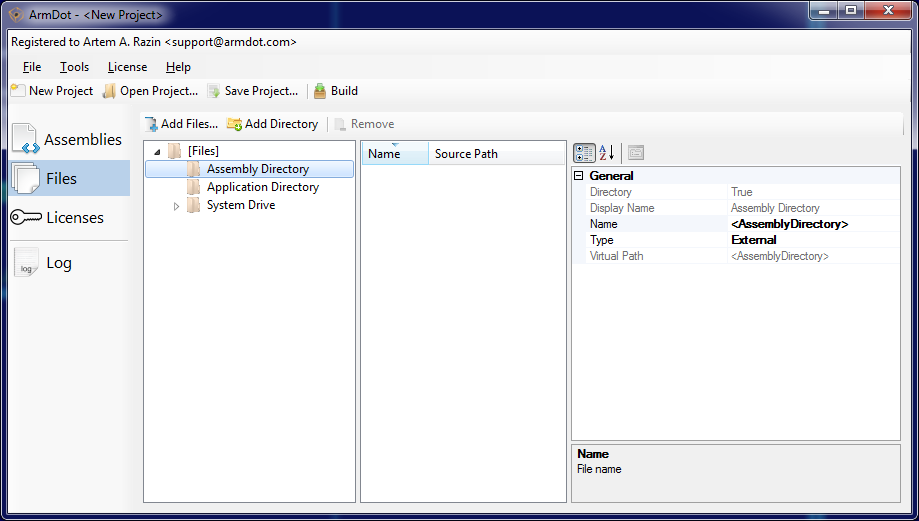
Here are the predefined folders at the right, like Assembly Directory and System Drive.
To include a file to a protected assembly click to Add Files... and choose the file. Another option is to import the entire directory.
Possible file / directory type is Embedded or External. To change it, select a file and change type via Properties on the right from the file tree.
If a directory is not marked as embedded, the protected assembly will view both real files and embedded files in the directory.